What is the Double Empathy Problem?
The Double Empathy Problem: Dissecting The Empathy Gap in Autistic Social Interactions
Understanding The Concept of Double Empathy
Defined in broad terms, double empathy abridges the theory that the social disconnect experienced between neurodivergent individuals, particularly those on the autism spectrum, and neurotypical individuals is a two-way street.
It’s not merely the autistic person’s inability to decode neurotypical social cues, but also the neurotypical person’s failure to acknowledge and respect the social cues of the autistic person.
This phenomenon, known as the double empathy problem, underscores the need for a greater understanding of autistic experiences and a deconstruction of societal norms.
The Significance of Recognizing The Double Empathy Problem
Why is it crucial to comprehend the double empathy problem?
The answer goes beyond establishing better communication channels; it lies in dismantling harmful stereotypes about autistic individuals.
It lays a foundation to challenge dominant societal norms and biases, fostering a more inclusive society.
Understanding the double empathy problem brings about a shift in perspective, highlighting the need to appreciate varied forms of social interaction and emotional connection.
Objectives of This Discussion
This comprehensive discourse aims to unravel and delve into the complexities surrounding the double empathy problem.
By using the lens of social cognition, and incorporating the Theory of Mind (often associated with the double empathy problem), we will attempt to elucidate the significance of emotional connection and mutual understanding challenges.
In addition, this discussion will draw parallels with autistic social experiences to shed light on the practical implications of the double empathy problem.
Furthermore, by establishing a connection between the double empathy problem and the broader scope of autistic social interaction, we aim to deepen awareness about the deeper context underpinning these experiences.
The goal is to foster empathy, encourage conversation, and ultimately, bridge the empathy gap between neurotypical and neurodivergent individuals.
Origin and Overview of The Double Empathy Problem

The Theory’s Establishment and Important Contributors
Pioneering Insights from Autistic Researchers
A defining factor in advancing the understanding of autistic experiences is the invaluable contribution of autistic researchers themselves.
One such influential figure is Dr. Damian Milton, who has made significant strides in redefining the discourse on autism, particularly in the context of empathy.
Notably, Dr. Milton, who is on the autism spectrum, introduced the concept of the “double empathy problem.“
Brief Introduction of Researcher Damian Milton
The Uniqueness of Dr. Damian Milton
Dr. Damian Milton, characterized by his first-hand experience of autism, has brought a distinctive and invaluable perspective to the academic and societal understanding of autism.
His commitment to this cause is demonstrated through his affiliation with the School for Education Research and Development at Canterbury Christ Church University and his participation in the research committee of the National Autistic Society.
His academic and advocacy work underscores his passion for advancing neurodivergent rights, fostering inclusion, and primarily focusing on enhancing autistic social interaction.
His Autistic Background and Contribution to The Theory
An Inside Perspective on Empathy Barriers
As an autistic individual, Damian Milton has a deep understanding of the fundamental barriers to empathetic communication that permeate everyday autistic life.
His experiences led him to dedicate his research efforts to bridging the empathy gap and unveiling the pervasive societal misunderstandings often erroneously attributed to an exclusive “autism problem.”
In his pursuit of a more accurate representation of autistic experiences, he introduced the groundbreaking concept of the double empathy problem.
The Initial Introduction and Acceptance of The Theory
Championing a Paradigm Shift
Like many pioneering theoretical propositions, the integration of the concept of the double empathy problem into mainstream psychological and sociological thought was met with some resistance.
Nevertheless, its undeniable relevance to the understanding of autism and its profound implications for acknowledging a two-way empathy deficit swiftly propelled it into the vanguard of autism research.
The theory challenged and reshaped previous assumptions about empathy and perspective-taking difficulties in autistic individuals, setting a new standard for comprehending the complexities of empathetic interactions in diverse neurological contexts.
Detailed Explanation of The Double Empathy Problem
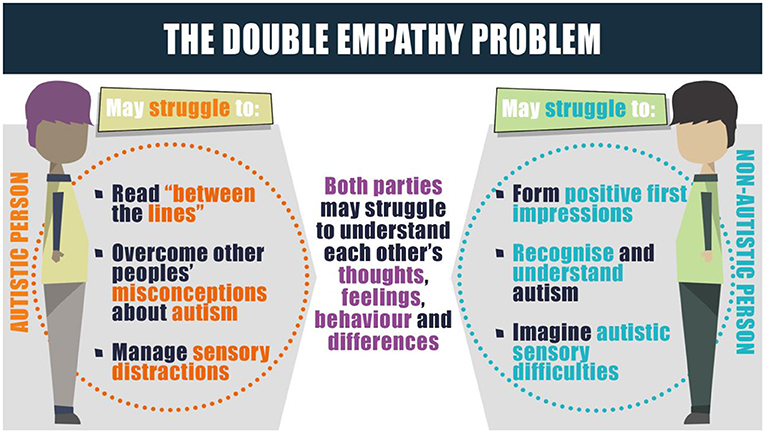
While often simply described as a failure of both neurotypical and autistic individuals to understand one another, the double empathy problem goes beyond mere social comprehension issues.
It dives deep into the contrasting ways neurodiverse and neurotypical individual process, perceive, and communicate social cues and emotions.
Discussing What It Is
The double empathy problem essentially is an acknowledgment of mutual understanding challenges between two different neurological makeups.
It contends that empathy is not inherently diminished in autistic individuals; rather, it is vastly different because of how diversely they experience, interpret, and interact with their social environment compared to non-autistic individuals.
Autism’s Unique Social Lens
Autistic individuals perceive the world through a unique social lens.
They often pay intense attention to detail, which can lead to a deeper understanding of specific subjects or situations.
However, in a social context, this intense focus might lead to challenges in comprehending broader, more nuanced social cues.
Autistic individuals may struggle with the unspoken rules and conventions that neurotypical individuals often take for granted.
Empathy as a Spectrum
The concept of empathy itself is more accurately described as a spectrum rather than a singular, universally defined trait.
Autistic individuals may express their empathy differently than their neurotypical counterparts, often in ways that are overlooked or misunderstood.
For instance, their empathy might be more evident in their commitment to specific interests or their willingness to provide practical support to others, rather than through conventional social gestures.
How It Impacts Autistic Individuals
Being at the receiving end of dominant social norms, autistic individuals face numerous disadvantages due to the double empathy problem.
They face unintentional social exclusion, are misunderstood, and often stigmatized as lacking empathy entirely.
These issues deepen the empathy gap, exacerbating their emotional connection issues.
Unintentional Social Exclusion
Autistic individuals, due to their unique way of processing social information, can often feel excluded from mainstream social interactions.
Neurotypical individuals may not be aware of the subtle cues and communication styles autistic individuals use, leading to unintentional exclusion.
Misunderstanding and Stigmatization
Autistic individuals frequently experience misunderstandings about their intentions and emotions.
Society’s expectation for certain social behaviors and cues can lead to a false belief that they lack empathy or emotional depth.
This misperception results in stigmatization, further alienating them.
How It Impacts Neurotypical Individuals
For neurotypical individuals, the effect of the double empathy problem often manifests as communication barriers.
It impairs their ability to genuinely grasp the unique perspective and autistic social experiences, leading to uninformed misconceptions about autistic behavior, emotion, and empathetic capacities.
Communication Barriers
Neurotypical individuals might find it challenging to effectively communicate with autistic individuals due to differences in social cues and communication styles.
This can create unintentional communication barriers that hinder mutual understanding.
Misconceptions About Autism
A lack of understanding of autistic social experiences can lead to misconceptions and stereotypes about autistic behavior.
These misconceptions can perpetuate societal misunderstandings, furthering the divide between neurotypical and autistic individuals.
Understanding the double empathy problem is essential in promoting more inclusive and empathetic interactions between neurodiverse and neurotypical individuals.
Recognizing that empathy is expressed diversely across different individuals and embracing these differences can bridge the gap and create a more compassionate society.
Scientific and Research-Based Evidence on The Double Empathy Problem
The double empathy problem is supported by academic research producing empirical evidence about its existence and effects.
Research studies generally focus on social cognition, emotional responses, and Theory of Mind, observing and examining both the autistic and neurotypical perspective.
Various Research Studies Carried Out
Numerous studies have been conducted to further explore the theory of the double empathy problem.
They utilize a vast array of methodologies, from neuroimaging to observe brain functions to social experiments, testing social interactions between autistic and non-autistic participants.
These studies contribute to the understanding of the equitable nature of the empathy chasm.
What These Studies Say about The Double Empathy Problem
Research data substantiates the existence of the double empathy problem.
Studies indicate that neurotypicals struggle just as much to interpret autistic communication signals, as autistic people do with neurotypical signals.
This evidences the theory’s argument of a two-way deafening empathy disconnect.
The issue remains not with autistic empathy, but with the differences in the ‘social languages’ spoken by autistic and non-autistic individuals.
In essence, it’s not about lack of empathy, as once suggested, but a divergence in empathetic expression and interpretation.
The double empathy problem urges society to recognize this divergence and initiate efforts for increased mutual understanding.
The Impact and Implications of The Double Empathy Problem

Explanation of The Societal Impacts
Breaking Down the Barriers to Understanding
The double empathy problem identifies an important issue at the heart of autism understanding: the struggle to bridge the gap between neurotypical and autistic individuals in society.
It goes beyond recognizing difficulties in social interaction and dives deep into the societal implications.
Misunderstandings and Miscommunications Between Autistic and Neurotypical Individuals
The core impact is the creation of a divide in social comprehension, leading to misinterpretations and miscommunications in everyday interactions.
This not only affects the quality and fluidity of communication but deepens misunderstandings about autistic individuals—fueling stereotypes and often causing self-esteem issues for autistic individuals due to constant misinterpretation.
Fostering Misinterpretations
The double empathy problem contributes to a dynamic in which misunderstandings and miscommunications proliferate.
Neurotypical individuals may struggle to grasp the nuances of autistic communication, and autistic individuals, in turn, may find it challenging to decipher the social cues of neurotypical communication.
This divergence in communication styles can result in well-intentioned but erroneous interpretations.
Fueling Stereotypes
A direct consequence of these ongoing misunderstandings is the perpetuation of stereotypes about autistic individuals.
Society’s failure to understand the unique forms of empathy and expression characteristic of autism leads to misconceptions.
Autistic individuals may be stigmatized as lacking empathy, which can harm their self-esteem and overall well-being.
The Societal Norms and Biases
The double empathy problem fosters an understanding that societal norms and biases often cater to neurotypical experiences.
In doing so, these norms force autistic individuals to adapt constantly, which can inhibit their natural modes of interaction and potentially exacerbate their emotional connection issues.
Adapting to a Neurotypical World
Societal norms are often constructed around neurotypical experiences and expectations.
This creates a constant pressure on autistic individuals to adapt to these norms, suppressing their natural way of interacting with the world.
The need to conform to neurotypical standards can be emotionally taxing and often results in an emotional connection gap.
Real-Life Examples of How Double Empathy Problem Affects Societal Relations
Examples of the double empathy problem’s societal impacts range from exclusion in social gatherings due to perceived ‘awkwardness’, to discriminatory practices in institutions where autistic modes of communication are not understood.
Furthermore, the misunderstanding of autistic emotional expression often leads to them being deemed insensitive or aloof—fueling the societal stereotype of ’emotionless’ autistics.
Exclusion in Social Settings
In everyday life, autistic individuals may experience exclusion from social gatherings due to perceived social ‘awkwardness.’
These situations are often the result of misunderstandings or misinterpretations of autistic behavior.
The failure to recognize and embrace diverse communication styles can lead to missed opportunities for social interaction.
Discriminatory Practices
Institutions that fail to understand and accommodate autistic modes of communication can inadvertently perpetuate discriminatory practices.
This occurs when standardized approaches do not cater to the unique needs of autistic individuals.
Discrimination in education, employment, and healthcare can further marginalize autistic individuals.
Stigmatization of Emotional Expression
The misunderstanding of how autistic individuals express their emotions can result in the unfair label of ‘insensitive’ or ‘aloof.’
Such stigmatization reinforces the societal stereotype that autistic individuals lack the capacity for deep emotional connections.
These misconceptions can lead to unfair treatment and a lack of empathy from society as a whole.
Recognizing and addressing the double empathy problem is essential in fostering a more inclusive and empathetic society.
By understanding the societal impacts of this issue, we can work towards a world that accommodates diverse forms of communication and promotes empathy for all, regardless of their neurodiversity.
The Personal Impact on Autistic Individuals
The double empathy problem is far-reaching in its implications, deeply infiltrating the psyche, emotional well-being, and lived experiences of autistic individuals.
It addresses their struggle within a predominantly neurotypical world while highlighting their immense strength and resilience.
The Difficulties Faced at Individual Level
At the individual level, the double empathy problem poses empathetic communication barriers, leading to feelings of isolation and challenges with self-expression.
The constant need to decode neurotypical behavior and the struggle to conform can cause stress and anxiety, impacting their overall well-being.
The Mental Health Concerns Tied to The Double Empathy Problem
The emotional strain posed by the double empathy problem can lead to mental health concerns for autistic individuals.
It fosters a sense of perennial alienation from societal norms, which may lead to self-esteem issues, social anxiety, and in some cases, depression.
Strategies Used by Autistic Individuals to Cope with Double Empathy Problem
Autistic individuals employ various strategies to cope with the double empathy problem.
Some tend to embrace their unique mode of interaction while educating others about it.
Others often find safe, understanding circles, such as autistic communities or supportive neurotypicals, providing emotional reprieve and genuine social connectedness.
The Effects on Professional Relationships
Professional settings are one of the most challenging areas for autistic individuals when navigating the double empathy problem.
These spaces, primarily designed for neurotypical interaction, pose tremendous difficulties for autistic professionals.
The Struggles Faced in Workplace Settings
Within professional environments, the double empathy problem can become especially prominent.
Miscommunication, misunderstanding, and difficulty working in standard office conditions can lead to discrimination, career stagnation, and in some instances, unemployment.
The Bridging of Understanding at Workplaces
Despite these challenges, there are growing efforts to bridge understanding in workplaces.
From seminars aimed at educating neurotypical employees about the double empathy problem, to implementing reasonable accommodations and autism-friendly policies, steps are being taken to create more inclusive and understanding professional environments.
Possible Solutions to The Double Empathy Problem
Educating the General Public
Education plays a paramount role in ousting the empathy gap between autistic and neurotypical individuals.
An informed public can make a world of difference in minimizing the mutual understanding challenges posed by the double empathy problem.
Role of Education in Understanding Diversity
The Power of Comprehensive Education
Education serves as a cornerstone in bridging the divide created by the double empathy problem. It extends beyond the classroom to permeate societal understanding and acceptance.
A comprehensive and inclusive education system is a powerful tool that can introduce neurodiversity to students from a young age.
This lays the groundwork for a generation more understanding of autism and more mindful of the double empathy problem.
Laying the Foundations of Empathy
The role of education in eradicating the double empathy problem involves two essential aspects.
The first is integrating neurodiversity content into the curriculum. By teaching students about autism and diverse forms of communication from an early age, we can foster acceptance and understanding.
The second aspect involves preparing teachers to guide diverse classrooms with empathy and competence.
Equipping educators with the knowledge and skills to create inclusive environments is a crucial step in addressing the double empathy problem at its core.
Role of Media in Promoting Understanding and Empathy
Shaping Societal Discourse
The media plays an influential role in shaping societal discourse.
From movies and television series to news reports and documentaries, media has the power to either reinforce harmful stereotypes or revolutionize understanding about autistic individuals.
By presenting a balanced, unbiased view of autism and the double empathy problem, the media can play an essential role in reshaping societal perception and debunking stereotypes.
Promoting Authentic Narratives
One of the media’s responsibilities is to present authentic narratives of autistic individuals.
These stories can provide a window into their experiences, perspectives, and challenges.
When media showcases the rich diversity within the autistic community and highlights the strengths and talents of individuals with autism, it can have a transformative impact on public perception.
How This Education Can Influence Societal Change
Creating Informed Citizens
Education brings about societal change by uprooting misconceptions and setting new, more inclusive norms.
Informed individuals will be more equipped to understand autistic social cues, promoting empathetic interactions and minimizing communication barriers.
This understanding and empathy can translate into more inclusive legislation, corporate policies, and societal accommodations for autistic individuals.
Shaping Legislation and Policies
As education fosters understanding, it can influence legislative changes. Informed citizens are more likely to advocate for policies that support and protect the rights of autistic individuals.
This can include legislation that promotes inclusive education, reasonable workplace accommodations, and accessibility in public spaces.
Fostering Inclusive Environments
The ultimate goal of education in combating the double empathy problem is to create a society where diversity is celebrated.
Informed and empathetic individuals can foster inclusive environments that accommodate diverse communication styles.
This shift can result in workplaces, educational institutions, and public spaces that are more welcoming and understanding of autistic individuals.
By focusing on education and media, we can address the double empathy problem at its roots and work toward a more inclusive and empathetic society.
These efforts have the potential to create a world where autistic and neurotypical individuals can connect, communicate, and thrive together.
Inclusion of Autistic Individuals in Decision Making
Central to resolving mutual understanding challenges is the inclusion of autistic individuals in decision-making.
Their lived experiences provide invaluable insights that can drive significant changes.
Importance of Diversity in Decision-Making Processes
Unlocking Diverse Perspectives
Diverse decision-making bodies, representing a spectrum of backgrounds and experiences, have the power to unlock innovative solutions.
When autistic individuals are included in these processes, their unique perspectives come to the forefront.
This inclusion ensures that proposed solutions cater to their specific needs and challenges, fostering a more empathetic and inclusive society.
Fostering Authentic Engagement
The importance of diversity in decision-making processes cannot be overstated.
Autistic individuals have a deep understanding of their own experiences, challenges, and strengths.
Their inclusion in decision-making facilitates authentic engagement and encourages autistic social interaction that aligns with their preferences.
This approach is a critical step toward bridging the gap created by the double empathy problem.
Benefits of Including Autistic Perspectives
Unique Solutions for Autistic Individuals
Incorporating autistic perspectives into decision-making processes yields multiple benefits.
Foremost, it leads to the creation of solutions that cater uniquely to autistic individuals.
This approach fosters tailored support and accommodation strategies, ensuring that autistic voices are not only heard but acted upon.
Enhancing Understanding and Empathy
Inclusion of autistic perspectives goes beyond tailored solutions; it fosters a deeper understanding of how to engage with the autistic community.
Decision-makers gain insights into the experiences, emotions, and sensory sensitivities of autistic individuals.
This newfound understanding informs strategies to cope with perspective-taking difficulties and paves the way for more empathetic interactions, ultimately reducing the impact of the double empathy problem.
Real-World Examples of Successful Inclusion
Champions of Inclusion
Numerous institutions and organizations have become champions of inclusion, setting remarkable examples of successful integration of autistic voices.
A notable case is the tech giant Microsoft, which has implemented an ‘autism hiring program.’
This program reflects a commitment to diverse perspectives in the workplace, highlighting the tangible benefits of such inclusion.
Autistic employees bring unique talents, problem-solving skills, and creative insights to the table, enriching the workforce.
Inclusive Education Initiatives
In the realm of education, inclusive schools have demonstrated substantial strides in fostering understanding and empathy among students.
These schools prioritize creating diverse and supportive learning environments where students of all abilities, including autistic individuals, learn side by side.
By promoting positive interactions and nurturing understanding from a young age, these institutions combat stereotypes and contribute to a more inclusive society.
The inclusion of autistic individuals in decision-making processes is a powerful step toward minimizing mutual understanding challenges.
Their perspectives lead to tailored solutions, enhance empathy, and foster a society where all individuals, regardless of neurodiversity, can engage and thrive together.
Advocacy for Improved Mental Health Resources
Mental health remains an area invariably linked with the double empathy problem.
Advocacy for improved mental health resources for autistic individuals is unquestionably crucial.
Explanation of The Current State of Mental Health Resources
Limitations of Existing Resources
Regrettably, the current state of mental health resources for autistic individuals is marked by limitations in both availability and adequacy.
Many mental health professionals lack the specialized training necessary to effectively address the unique emotional and psychological needs of autistic individuals.
As a result, care often falls short of meeting their requirements, accentuating the profound impact of the double empathy problem on their mental health.
The Changing Landscape
Despite these challenges, there is hope on the horizon.
In recent years, there has been an increased focus on mental health within the autistic community.
This heightened awareness has been instrumental in illuminating the shortcomings of current resources and highlighting the pressing need for improvement.
Consequently, strides are being taken to reform the landscape of mental health resources and provide more effective support for autistic individuals.
Presentation of Case Studies or Examples of Successful Mental Health Interventions
Several successful mental health interventions provide a beacon of hope for improved resources.
Somatic therapy, for instance, has shown success in helping autistic individuals in managing stress and anxiety.
There are organizations dedicated to comprehending the intricate interplay between autism and mental health.
By offering tailored mental health services, they address the unique concerns linked to the double empathy problem.
Such specialized support initiatives mark a promising shift in mental health resources, recognizing that autistic individuals require distinct and empathetic care.
Advocacy for improved mental health resources represents a critical step in addressing the double empathy problem and its impact on the mental well-being of autistic individuals.
As more effective interventions and specialized support systems emerge, the path toward enhanced mental health care becomes increasingly clear.
Reflecting on the Gravity of The Double Empathy Problem
Through this in-depth exploration, we gain a deeper understanding of just how profound the double empathy problem is and the extent of its implications.
At the heart of this issue is a fundamental breakdown in mutual understanding, a disjunctive conversation where both parties struggle to comprehend each other’s perspective and language.
Despite its challenges, the double empathy problem pushes us towards a more inclusive and empathetic lens for examining autistic experiences.
It urges us to view autistic social interaction not as ‘inferior’ but just as ‘different’, just as capable of nuance, emotion, and indeed empathy.
It tiresomely demonstrates that the empathy gap is not a one-way street, but an issue of mutual misunderstanding.
All too often, the communication and social comprehension problems that arise because of the double empathy problem are attributably single-sided to the autistic community—further marginalizing them.
However, this cannot be further from the truth. The double empathy problem reminds us that neurotypical individuals play a significant role in exacerbating or narrowing this gap.
As our perspective broadens, we must also focus on gains made despite these difficulties.
Through this lens, we observe the resilience and strength of autistic individuals, their constant adaptations, and the vibrant diversity they bring to societal understanding.
Each day, they negotiate an environment that is often alien to their innate being and yet they persist—pioneering paths of acceptance and respect in their wakes.
Advocating for Change in Society
Each one of us has a role to play in resolving the double empathy problem—we are all vital threads in the societal fabric.
By raising awareness, we instigate the essential first step towards change. Start by educating yourself about the double empathy problem and autistic experiences, then share this knowledge with others.
Consider the media you consume and share, think about whether it fosters understanding or perpetuates harmful stereotypes.
Moreover, actively participating in advocacy for more inclusive policies—within educational systems, workplaces, and legislatures—is crucial.
Advocate for the inclusion of autistic voices in these venues; their perspectives are an underutilized but potent tool for instigating profound change.
Mental health awareness is another area where advocacy is crucial. The emotional toll from constantly navigating the double empathy problem is considerable.
Encourage local mental health professionals to educate themselves about the unique mental health concerns tied to the double empathy problem in order to provide more efficient and effective care.
All in all, remember empathy itself is the starting point. The précis of the double empathy problem is in its name: empathy.
Begin with extending yours, by imagining and understanding the experiences of autistic individuals.
This empathy, coupled with active advocacy and widespread education, can help to overcome the double empathy problem—fostering a more understanding and inclusive society.