For many autistic people, there comes a point where everything starts to collapse, energy, language, motivation, and even the ability to function in day-to-day life. You might ask yourself: “Am I just depressed? Or is this something else?”
That’s where the concept of autistic burnout comes in. Though not yet an official diagnosis in clinical manuals, it’s widely recognized by autistic people and increasingly studied in academic circles (Raymaker et al., 2020). It often shares symptoms with clinical depression, which can lead to confusion, misdiagnosis, and inadequate care.
But here’s the truth: while there’s overlap, autistic burnout and depression are not the same thing. Knowing the difference can change how we support, recover, and relate to ourselves.
What Is Autistic Burnout?
Autistic burnout is a state of profound physical, mental, and emotional exhaustion experienced by autistic individuals, usually as a result of prolonged masking, sensory overwhelm, and unmet support needs.
Raymaker et al. (2020) define autistic burnout as involving three core features:
Chronic exhaustion
Loss of skills (e.g., speech, executive functioning)
Increased sensory sensitivity
Unlike typical burnout, autistic burnout is often long-lasting and deeply tied to identity and environment, not just workload.
People experiencing autistic burnout often describe:
Trouble forming words or expressing thoughts
Intense fatigue that sleep doesn’t fix
Sensory overload
Emotional numbness or shutdown
Difficulty performing even basic tasks like showering or cooking
This isn’t “just stress” or laziness. It’s a physiological and cognitive collapse caused by long-term overstimulation and social pressure.
What Causes Autistic Burnout?
Burnout often comes after extended periods of masking, that is, hiding autistic traits to “blend in” socially, which has been shown to increase rates of anxiety, exhaustion, and suicidality (Cage & Troxell-Whitman, 2019).
Other contributing factors include:
Lack of accommodations or understanding in school/workplace
Constant sensory overload (noise, lighting, touch)
Social rejection or the pressure to perform neurotypical behavior
A mismatch between needs and the environment
Over time, these stressors chip away at energy and resilience, leaving the nervous system depleted.
What Is Depression?
Clinical depression, or major depressive disorder (MDD), is a well-defined mental health condition involving persistent low mood, lack of pleasure, hopelessness, and physical symptoms like fatigue and changes in sleep or appetite.
It affects about 21 million adults in the U.S. alone (NIH, 2022), and it’s common among autistic people, some estimates suggest rates are 4x higher than in non-autistic populations (Hudson et al., 2019).
Common symptoms include:
Persistent sadness or irritability
Loss of interest in previously enjoyable activities
Feelings of worthlessness or guilt
Thoughts of death or suicide
Trouble sleeping or oversleeping
Physical aches without clear cause
Many of these symptoms look similar to autistic burnout, but the cause and the path to recovery are often different.
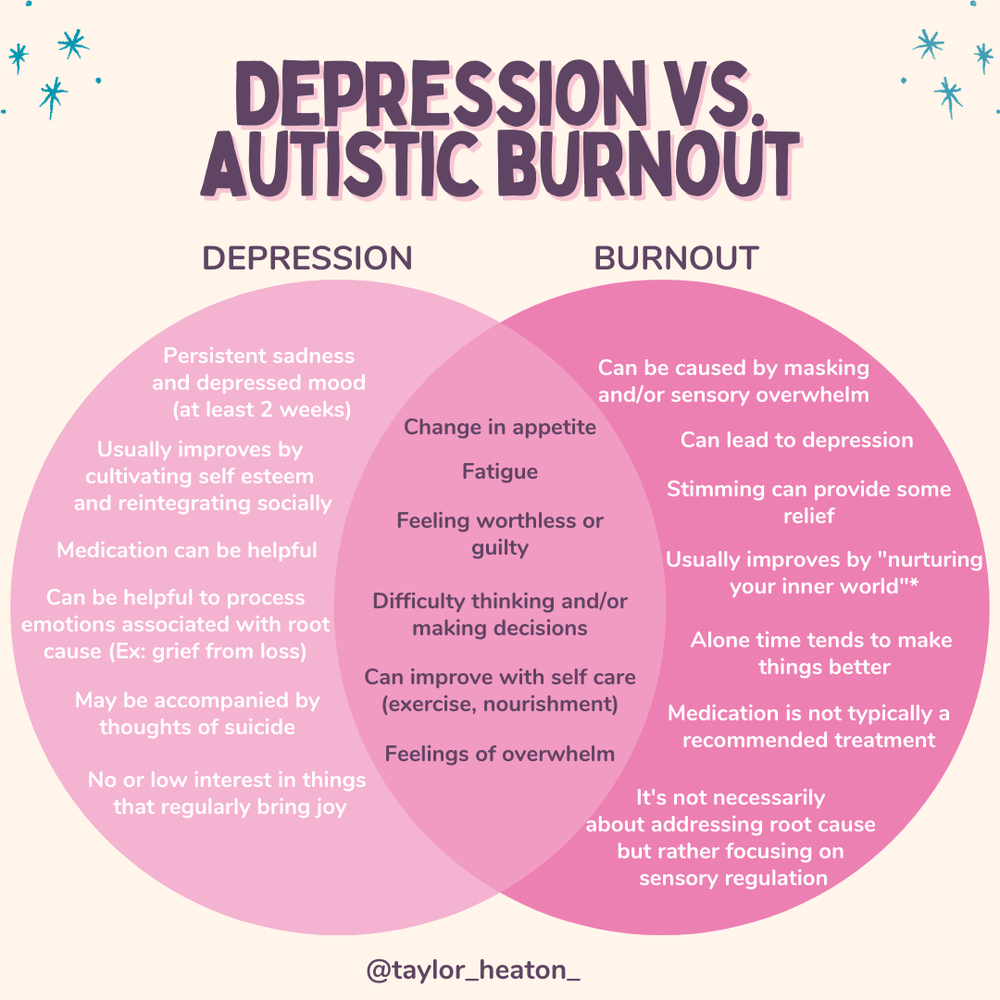
How They Overlap
Autistic Burnout and Depression can share symptoms, such as:
Low energy
Reduced motivation
Withdrawal from others
Difficulty focusing
Changes in eating and sleeping patterns
Emotional flatness or shutdown
Both can feel isolating and difficult to explain to others. And both deserve care and support. But confusing one for the other can lead to the wrong treatment.
Autistic Burnout vs. Depression
| Aspect | Autistic Burnout | Depression |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Long-term masking, sensory overload, unmet needs | Complex interaction of biological, psychological, and social factors |
| Duration | Can last weeks to years, especially if stressors persist | Varies, but often episodic with potential for recurrence |
| Recovery Needs | Rest, reduced demands, sensory regulation, self-acceptance | Therapy, medication, behavioral activation |
| Loss of Skills | Often includes temporary regression (e.g., loss of speech or coping mechanisms) | Less common outside of extreme cases |
| Identity Tied | Deeply tied to autistic traits and chronic environmental stress | Not identity-based, more mood and brain chemistry driven |
Why It Matters to Get the Diagnosis Right
Many autistic people have been misdiagnosed with depression when they were experiencing burnout, and then prescribed treatments that made things worse, not better.
Antidepressants may help with mood but don’t address sensory overload or chronic masking.
Talk therapy may fall flat if it doesn’t recognize autistic communication styles.
Being told to “push through” can deepen burnout.
On the other hand, recognizing burnout for what it is can shift the entire approach: toward gentleness, low-demand environments, unmasking, and recharging.
What Helps with Autistic Burnout?
According to the autistic community and emerging research, some effective supports include:
Time off from masking
Low-stimulation environments
Validating spaces or neurodivergent community support
Sensory tools (weighted blankets, noise-canceling headphones)
Self-compassion and reduced self-judgment
Working with neurodivergent-affirming therapists
Burnout isn’t fixed by “trying harder.” It’s helped by being allowed to stop trying so hard.
What Helps with Depression?
While every person is different, treatments for depression may include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Antidepressant medication
Exercise and behavioral activation
Supportive relationships
Sleep regulation and nutrition
These interventions can also be helpful for autistic people, but only if burnout and autistic needs are also addressed. Otherwise, there’s a risk of treating the wrong issue.
Final Thoughts
You’re not making it up. You’re not lazy. Whether you’re dealing with autistic burnout, depression, or both, they’re real, valid, and worthy of care.
The truth is, many autistic people will experience both at some point. That’s why it’s so important to understand the distinction, not to label or box anyone in, but to find the right kind of help.
Autistic burnout doesn’t mean you’re broken. It often means you’ve been pushing too hard, for too long, in a world that hasn’t made enough room for who you are.
Let’s change that.
Sources:
Raymaker, D. M., Teo, A. R., Steckler, N. A., et al. (2020). “Having All of Your Internal Resources Exhausted Beyond Measure and Being Left with No Clean-Up Crew”: Defining Autistic Burnout. Autism in Adulthood, 2(2), 132–143. https://doi.org/10.1089/aut.2019.0079
Cage, E., & Troxell-Whitman, Z. (2019). Understanding the Reasons, Contexts and Costs of Camouflaging for Autistic Adults. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 49, 1899–1911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-018-03878-x
Hudson, C. C., Hall, L., & Harkness, K. L. (2019). Prevalence of Depressive Disorders in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 47, 165–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-018-0402-1
National Institute of Mental Health. (2022). Major Depression. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/major-depression